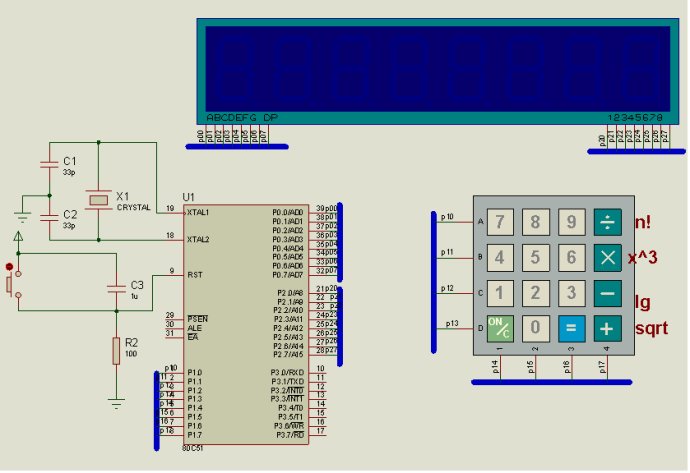
一、硬件仿真图
二、主程序流程图 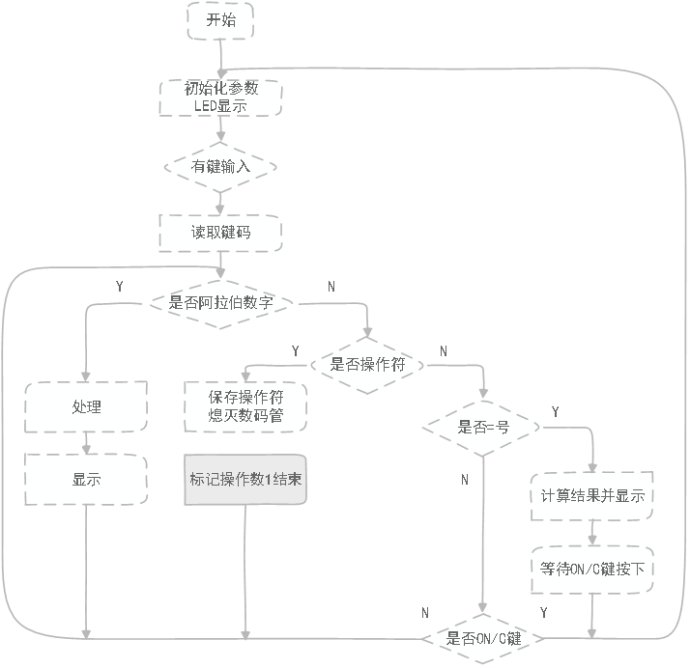
程序的主要思想是:将按键抽象为字符,然后就是对字符的处理。将操作数分别转化为字符串存储,操作符存储为字符形式。然后调用compute()函数进行计算并返回结果。具体程序及看注释还有流程图。
三、程序源代码
#include <reg51.h>#include <intrins.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define uchar unsigned char
#define uint unsigned int
uchar operand1[9], operand2[9];
uchar operator;
void delay(uint);
uchar keyscan();
void disp(void);
void buf(uint value);
uint compute(uint va1,uint va2,uchar optor);
uchar code table[] = {0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,
0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90,0xff};
uchar dbuf[8] = {10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10};
void delay(uint z)
{
uint x,y;
for(x=z;x>0;x--)
for(y=110;y>0;y--);
}
uchar keyscan()
{
uchar skey;
P1 = 0xfe;
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
delay(3);
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
switch(P1)
{
case 0xee: skey = '7'; break;
case 0xde: skey = '8'; break;
case 0xbe: skey = '9'; break;
case 0x7e: skey = '/'; break;
default: skey = '#';
}
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
;
}
}
P1 = 0xfd;
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
delay(3);
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
switch(P1)
{
case 0xed: skey = '4'; break;
case 0xdd: skey = '5'; break;
case 0xbd: skey = '6'; break;
case 0x7d: skey = '*'; break;
default: skey = '#';
}
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
;
}
}
P1 = 0xfb;
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
delay(3);
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
switch(P1)
{
case 0xeb: skey = '1'; break;
case 0xdb: skey = '2'; break;
case 0xbb: skey = '3'; break;
case 0x7b: skey = '-'; break;
default: skey = '#';
}
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
;
}
}
P1 = 0xf7;
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
delay(3);
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
{
switch(P1)
{
case 0xe7: skey = '$'; break;
case 0xd7: skey = '0'; break;
case 0xb7: skey = '='; break;
case 0x77: skey = '+'; break;
default: skey = '#';
}
while((P1 & 0xf0) != 0xf0)
;
}
}
return skey;
}
void main()
{
uint value1, value2, value;
uchar ckey, cut1 = 0, cut2 = 0;
uchar operator;
uchar i, bool = 0;
init:
buf(0);
disp();
value = 0;
cut1 = cut2 = 0;
bool = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 9;i++)
{
operand1[i] = '�';
operand2[i] = '�';
}
while(1)
{
ckey = keyscan();
if(ckey != '#')
{
if(isdigit(ckey))
{
switch(bool)
{
case 0:
operand1[cut1] = ckey;
operand1[cut1+1] = '�';
value1 = atoi(operand1);
cut1++;
buf(value1);
disp();
break;
case 1:
operand2[cut2] = ckey;
operand2[cut2+1] = '�';
value2 = atoi(operand2);
cut2++;
buf(value2);
disp();
break;
default: break;
}
}
else if(ckey=='+'||ckey=='-'||ckey=='*'||ckey=='/')
{
bool = 1;
operator = ckey;
buf(0);
dbuf[7] = 10;
disp();
}
else if(ckey == '=')
{
value = compute(value1,value2,operator);
buf(value);
disp();
while(1)
{
ckey = keyscan();
if(ckey == '$')
goto init;
else
{
buf(value);
disp();
}
}
}
else if(ckey == '$')
{ goto init;}
}
disp();
}
}
uint compute(uint va1,uint va2,uchar optor)
{
uint value;
switch(optor)
{
case '+' : value = va1+va2; break;
case '-' : value = va1-va2; break;
case '*' : value = va1*va2; break;
case '/' : value = va1/va2; break;
default : break;
}
return value;
}
void buf(uint val)
{
uchar i;
if(val == 0)
{
dbuf[7] = 0;
i = 6;
}
else
for(i = 7; val > 0; i--)
{
dbuf[i] = val % 10;
val /= 10;
}
for( ; i > 0; i--)
dbuf[i] = 10;
}
void disp(void)
{
uchar bsel, n;
bsel=0x01;
for(n=0;n<8;n++)
{
P2=bsel;
P0=table[dbuf[n]];
bsel=_crol_(bsel,1);
delay(3);
P0=0xff;
}
}
